Error analysis
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Error analysis is the study of kind and quantity of error that occurs, particularly in the fields of applied mathematics (particularly numerical analysis), applied linguistics and statistics.
For instance, in a system modeled as a function of two variables . Error analysis deals with the propagation of the numerical errors in
. Error analysis deals with the propagation of the numerical errors in  and
and  (around mean values
(around mean values  and
and 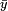 ) to error in
) to error in  (around a mean
(around a mean  ).[1]
).[1]
In numerical analysis, error analysis comprises both forward error analysis and backward error analysis. Forward error analysis involves the analysis of a function which is an approximation (usually a finite polynomial) to a function
which is an approximation (usually a finite polynomial) to a function  to determine the bounds on the error in the approximation; i.e., to find
to determine the bounds on the error in the approximation; i.e., to find  such that
such that 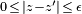 . Backward error analysis involves the analysis of the approximation function
. Backward error analysis involves the analysis of the approximation function  , to determine the bounds on the parameters
, to determine the bounds on the parameters  such that the result
such that the result  .[2]
.[2]
For a series of M measurements of a fluctuating property A, the mean value is:
 is the autocorrelation function defined by
is the autocorrelation function defined by
Contents
Error analysis in numerical modeling
In numerical simulation or modeling of real systems, error analysis is concerned with the changes in the output of the model as the parameters to the model vary about a mean.For instance, in a system modeled as a function of two variables
 . Error analysis deals with the propagation of the numerical errors in
. Error analysis deals with the propagation of the numerical errors in  and
and  (around mean values
(around mean values  and
and 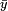 ) to error in
) to error in  (around a mean
(around a mean  ).[1]
).[1]In numerical analysis, error analysis comprises both forward error analysis and backward error analysis. Forward error analysis involves the analysis of a function
 which is an approximation (usually a finite polynomial) to a function
which is an approximation (usually a finite polynomial) to a function  to determine the bounds on the error in the approximation; i.e., to find
to determine the bounds on the error in the approximation; i.e., to find  such that
such that 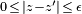 . Backward error analysis involves the analysis of the approximation function
. Backward error analysis involves the analysis of the approximation function  , to determine the bounds on the parameters
, to determine the bounds on the parameters  such that the result
such that the result  .[2]
.[2]Error analysis in second language acquisition
Main article: Error analysis (linguistics)
In second language acquisition, error analysis studies the types and causes of language errors. Errors are classified[3] according to:- modality (i.e., level of proficiency in speaking, writing, reading, listening)
- linguistic levels (i.e., pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary, style)
- form (e.g., omission, insertion, substitution)
- type (systematic errors/errors in competence vs. occasional errors/errors in performance)
- cause (e.g., interference, interlanguage)
- norm vs. system
Error analysis in molecular dynamics simulation
In molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, there are errors due to inadequate sampling of the phase space or infrequently occurring events, these lead to the statistical error due to random fluctuation in the measurements.For a series of M measurements of a fluctuating property A, the mean value is:
 is the autocorrelation function defined by
is the autocorrelation function defined bySee also
- Error analysis (linguistics)
- Error bar
- Errors and residuals in statistics
- Propagation of uncertainty
References
- Jump up ^ James W. Haefner (1996). Modeling Biological Systems: Principles and Applications. Springer. pp. 186–189. ISBN 0412042010.
- Jump up ^ Francis J. Scheid (1988). Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Numerical Analysis. McGraw-Hill Professional. p. 11. ISBN 0070552215.
- Jump up ^ Cf. Bussmann, Hadumod (1996), Routledge Dictionary of Language and Linguistics, London: Routledge, s.v. error analysis. A comprehensive bibliography was published by Bernd Spillner (1991), Error Analysis, Amsterdam/Philadelphia: Benjamins.
- Jump up ^ Corder, S. P. (1967). "The significance of learners' errors". International Review of Applied Linguistics 5: 160–170.
- Jump up ^ D. C. Rapaport, The Art of Molecular Dynamics Simulation, Cambridge University Press.
External links
- [1] All about error analysis.


![\sigma^{2}( \langle A \rangle ) = \frac{1}{M} \sigma^{2}A \left[ 1 + 2 \sum_\mu \left( 1 - \frac{\mu}{M} \right) \phi_{\mu} \right],](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/0/e/1/0e1603d7b9e6eb25a6e8c6da7762113c.png)

Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar